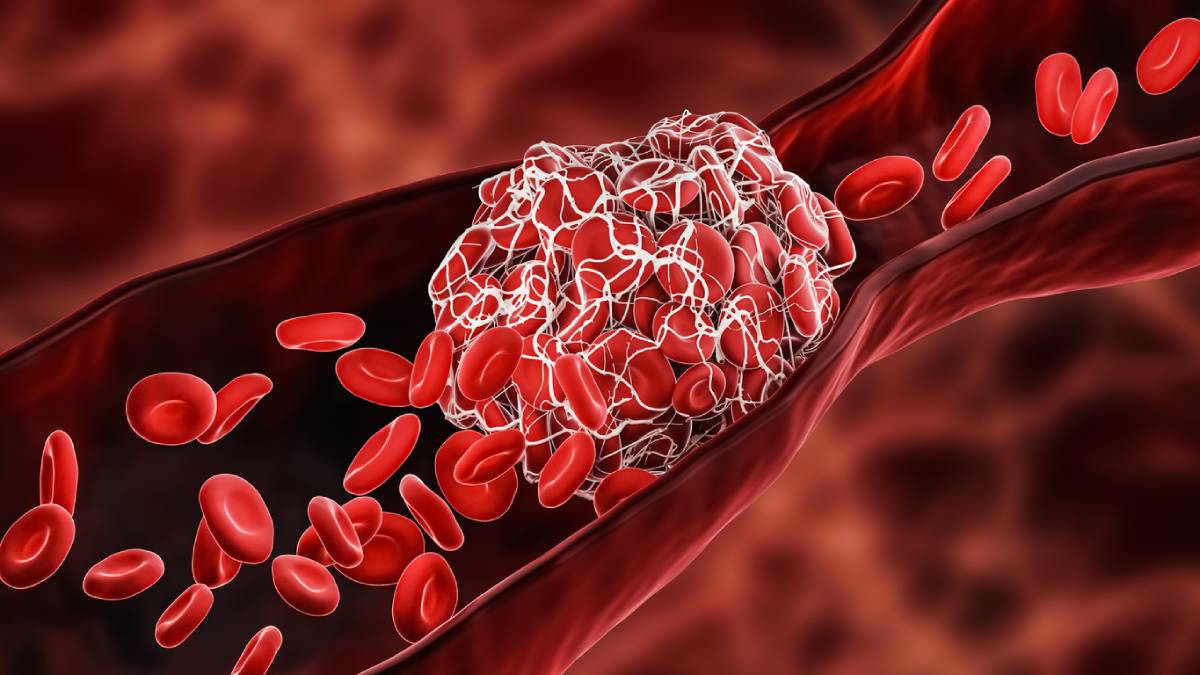
Deep vein thrombosis, otherwise known as DVT, is a condition that occurs as the result of a blood clot within the veins. While DVT can occur without symptoms, it is typical for those with this condition to feel swelling and pain in affected areas. Deep vein thrombosis is serious and can lead to a pulmonary embolism, or other fatal conditions if left untreated. Stay alert for these risk factors for DVT.
Risk Factors for DVT
Today, your vein and cardio specialist will discuss the biggest risk factors for DVT that you should be aware of. Even if you aren’t exhibiting symptoms, you should contact your specialist to make sure your blood is in a good state of health.
Symptoms of DVT
In order to better understand the best treatments for deep vein thrombosis, it is a good idea to learn how to identify some of its most unique symptoms. While it’s true that some patients do not experience symptoms right away, it is more likely to become symptomatic as the condition gets worse.
Common symptoms of deep vein thrombosis include:
- Pain or cramping in the legs
- Swelling of the legs up to a larger size
- Discomfort in the legs from the calf to the foot
- Warmth or bruising around the legs
- Skin color changes, typically to red or purple depending on your skin tone and the level of oxygen loss
You should contact your doctor at the first sign of any symptoms regarding pain or discomfort in your legs. If your symptoms worsen and you start to feel shortness of breath, a rapid pulse, or you experience fainting, you may need to visit the emergency room and seek treatment for a pulmonary embolism.
Biggest Risk Factors for DVT
Your doctor will prescribe a treatment for you based not only on the symptoms of DVT but also on the particular cause. It is important to analyze your family and medical history to determine if one of these risk factors is present in your life:
Family History
Unfortunately, genetics plays a big role in determining your likelihood of developing a condition like DVT. While your DNA changes throughout your life, you may be more prone to blood clots and therefore must take bigger precautions to avoid any medical complications with your blood.
Heart Complications
If you have been diagnosed with heart failure or have had heart complications in the past, you have an increased likelihood of developing DVT. Not only is a history of heart failure linked with DVT, but the disease leads to weakened lungs which can make it more difficult for the body to pump blood.
Aging
Unfortunately, the risk for deep vein thrombosis only increases as you get older. Those aged 60 or older are automatically at a higher risk for developing DVT due to complications the body faces during the aging process. If you are not already in contact with a specialist who can help monitor your body for signs of DVT as you age, you should do so ASAP.
Prevent and Treat DVT Today
If you are at risk of developing deep vein thrombosis but have not started displaying symptoms, you may be able to take steps to prevent this condition altogether. Make sure to keep your legs moving often, especially if you are often sitting or laying down during the day. Get out of the car and walk around if you can during days of long travel.
Managing your lifestyle choices, such as smoking and drinking, can significantly lower your risk of developing blood clots or issues with deep vein thrombosis. No matter your ability to exercise and move around daily, it is a good idea to have a regular routine that keeps your heart and veins healthy. Learn more about our variety of deep vein thrombosis treatment options when you get in touch with us today.